Disentangling Time Series Representations via Contrastive Independence-of-Support on l-Variational Inference
tl;dr: This work disentangles factors in time series data, allowing better understanding and optimization. It handles real-world correlations between factors and introduces TDS (Time Disentangling Score) to measure disentanglement quality effectively.
News
| May '21 | The paper was accepted at ICLR 2024 🚀🚀! |
| February '21 | The pre-print is now available on arXiv: arxiv.org/abs/2102.08850 |
| December '20 | A shorter workshop version of the paper was accepted for spotlight 🥇 presentation at the NeurIPS 2023 Workshop on Unifying Representations in Neural Models. |
Abstract
Learning disentangled representations is crucial for Time Series, offering benefits like feature derivation and improved interpretability, thereby enhancing task performance. We focus on disentangled representation learning for home appliance electricity usage, enabling users to understand and optimize their consumption for a reduced carbon footprint. Our approach frames the problem as disentangling each attribute’s role in total consumption (e.g., dishwashers, fridges, etc). Unlike existing methods assuming attribute independence, we acknowledge real-world time series attribute correlations, like the operating of dishwashers and washing machines during the winter season. To tackle this, we employ weakly supervised contrastive disentanglement, facilitating representation generalization across diverse correlated scenarios and new households. Our method utilizes innovative l-variational inference layers with self-attention, effectively addressing temporal dependencies across bottom-up and top-down networks. We find that DIoSC (Disentanglement and Independence-of-Support via Contrastive Learning) can enhance the task of reconstructing electricity consumption for individual appliances. We introduce TDS (Time Disentangling Score) to gauge disentanglement quality. TDS reliably reflects disentanglement performance, making it a valuable metric for evaluating time series representations.
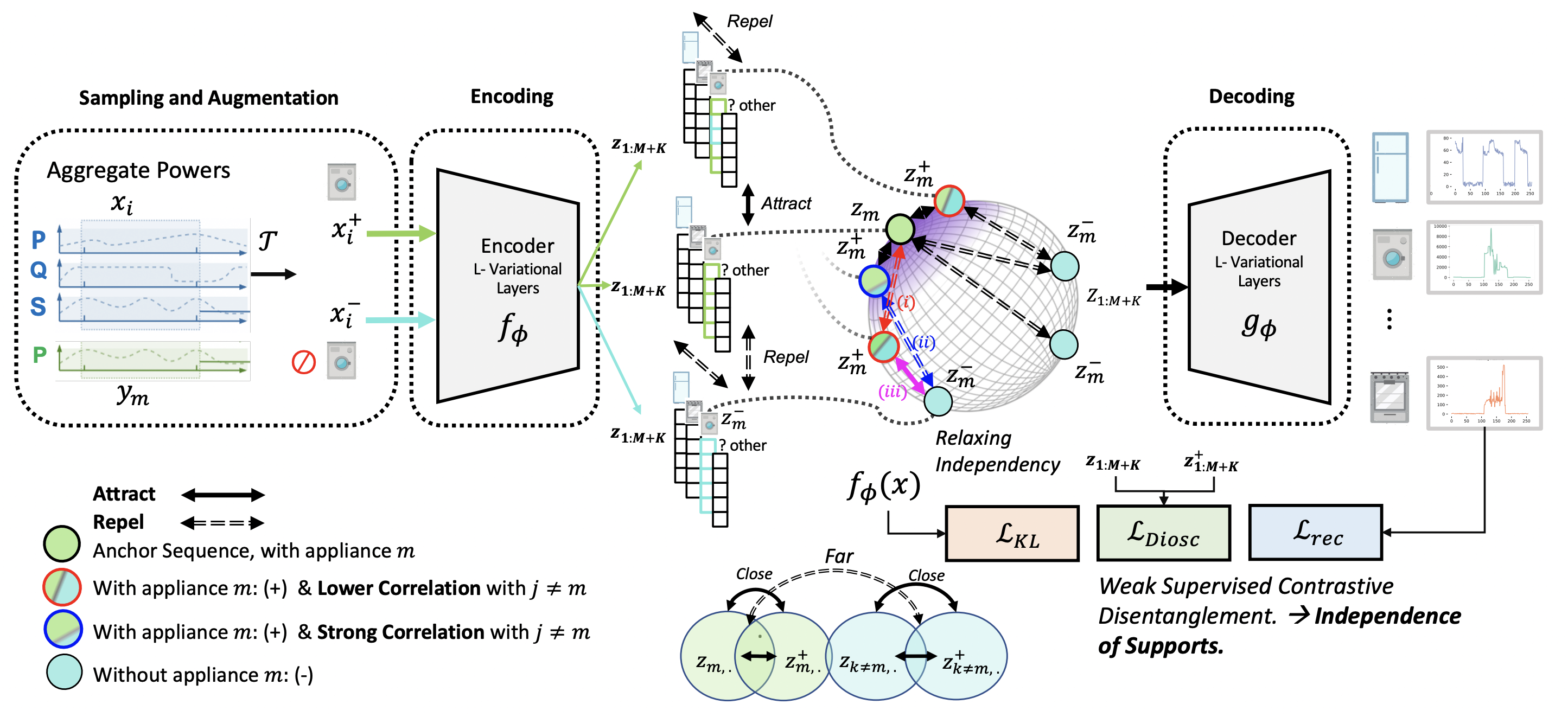 Overview: We focus on disentangled representation learning for home appliance electricity usage, enabling users to understand and optimize their consumption for a reduced carbon footprint. Our approach frames the problem as disentangling each attribute’s role in total consumption (e.g., dishwashers, fridges,
etc). Unlike existing methods assuming attribute independence, we acknowledge
real-world time series attribute correlations, like the operating of dishwashers and
washing machines during the winter season.
Overview: We focus on disentangled representation learning for home appliance electricity usage, enabling users to understand and optimize their consumption for a reduced carbon footprint. Our approach frames the problem as disentangling each attribute’s role in total consumption (e.g., dishwashers, fridges,
etc). Unlike existing methods assuming attribute independence, we acknowledge
real-world time series attribute correlations, like the operating of dishwashers and
washing machines during the winter season.
Contributions
- We establish a theoretical connection between the InfoNCE family of objectives, which is commonly used in self-supervised learning, and nonlinear ICA. We show that training with InfoNCE inverts the data-generating process if certain statistical assumptions on the data generating process hold.
- We empirically verify our predictions when the assumed theoretical conditions are fulfilled. In addition, we show a successful inversion of the data-generating process even if theoretical assumptions are partially violated.
- We build on top of the CLEVR rendering pipeline (Johnson et al., 2017) to generate a more visually complex disentanglement benchmark, called 3DIdent, that contains hallmarks of natural environments (shadows, different lighting conditions, a 3D object, etc.). We demonstrate that a contrastive loss derived from our theoretical framework can identify the ground-truth factors of such complex, high-resolution images.
Theory
To achieve disentanglement, invariant, and aligned latent representations, we use a contrastive objective that ensures each latent component \(z_m\) is only influenced by its corresponding output in the decoder. Specifically, disentanglement is achieved when each ground truth variable \(y_m\) aligns one-to-one with \(z_m\), even with limited labels in settings like NILM (Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring).
We build on weakly supervised contrastive learning, using an objective modified from Zbontar et al. (2021). This objective enforces two core components:
- Latent-Invariant: Minimizes overlap between \(z_m\) and its negatives \(z_m^{-}\), reducing redundant information.
- Latent-Alignment: Encourages similarity between \(z_m\) and its augmented \(z_m^{+}\), ensuring variations align with changes in ground truth attributes.
We empirically relax independence assumptions (Assumption 4.1) by enforcing independence of support (IoS) in mini-batches, ensuring that augmented latents \(Z_{:,m}^+\) are close to their original \(Z_{:,m}\) and far from negatives \(Z_{:,m}^-\), without requiring Cartesian product support.
The final objective combines these components: \[ L_{\text{DIOSC}} = \eta \sum_m \sum_V D(z_m, z_m^{-})^2 \, |_{\text{Latent-Invariant}} + \sum_m \sum_U \left(1 - D(z_m, z_m^{+})\right)^2 \, |_{\text{Latent-Alignment}}, \] where \(D(\cdot, \cdot)\) denotes cosine similarity distance, and \(\eta = 1\).
Dataset
We conducted experiments on three public datasets:
UK-DALE (Kelly & Knottenbelt, 2015),
REDD (Kolter & Johnson, 2011),
REFIT (Murray et al., 2017)
These datasets provide power measurements from multiple homes.
We focus on six appliances:
- Washing Machine
- Oven
- Dishwasher
- Cloth Dryer
- Fridge
We performed cross-tests on different dataset scenarios, each with varying sample sizes:
Scenario A: Training on REFIT and testing on UK-DALE
Sample Size: 18.3k | Time Window (T) = 256 | Frequency = 60Hz
Test Set: 3.5k samples
Scenario B: Training on UK-DALE and testing on REFIT
Sample Size: 13.3k
Scenario C: Training on REFIT and testing on REDD
Sample Size: 9.3k
The augmentation pipeline is applied for all scenarios. For training and testing under correlation, we use the corresponding sampling.
Acknowledgements & Funding
This work was granted access to the HPC resources of IDRIS under the allocation AD011014921 made by GENCI (Grand Equipement National de Calcul Intensif). Part of this work was funded by the TotalEnergies Individual Fellowship through One Tech.
BibTeX
If you find our analysis helpful, please cite our paper:
@inproceedings{oublal2024disentangling,
author = {
Oublal, Khalid and
Ladjal, Said and
Benhaiem, David and
LE BORGNE, Emmanuel and
Roueff, François
},
title = {
Disentangling Time Series Representations via Contrastive Independence-of-Support on l-Variational Inference
},
booktitle = {
The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations
},
year = {2024},
url = {
https://openreview.net/forum?id=iI7hZSczxE
}
}